PMR
Belajar Sains dengan perasaan ingin tahu
Chapter 1: Introduction to Sciences( Physical Quantities & SI Units)
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE ( PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AND SI UNIT )
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE ( SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION )
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE
Chapter 1: Introduction to Science (Measuring Tools)
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE (MEASURING TOOLS)
Chapter 1: Introduction to Science (Scientific Investigation) Mixed-up sentence exercise
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE
Chapter 2: Cell as a Unit of Life ( Cell Structures & Functions)
CELL AS A UNIT OF LIFE
CELL AS A UNIT OF LIFE ( CELL STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS )
CELL AS A UNIT OF LIFE
Chapter 2: Cell as a unit of Life ( Organs & Respective Systems)
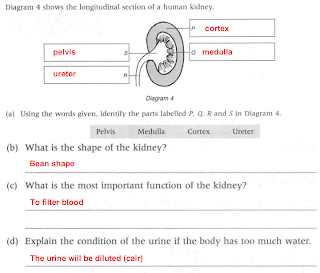
CELL AS A UNIT OF LIFE ( ORGANS AND RESPECTIVE SYSTEMS )
CELL AS A UNIT OF LIFE
MATTER
MATTER
MATTER
THE VARIETY OF RESOURCES ON EARTH
THE VARIETY OF RESOURCES ON EARTHv
THE VARIETY OF RESOURCES ON EARTH
THE VARIETY OF RESOURCES ON EARTH
AIR POLLUTION
THE AIR AROUND US
THE AIR AROUND US
THE AIR AROUND US
THE AIR AROUND US
Sources of energy
Energy changes
SOURCES OF ENERGY
SOURCES OF ENERGY
SOURCES OF ENERGY
Effect of Heat on Matter
HEAT
HEAT
HEAT
DYNAMICS
DYNAMICS 2
DYNAMICS 3
DYNAMICS 4
DYNAMICS 5
SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT
SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT 2
SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT 3
SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT 4
STABILITY
STABILITY 2
STABILITY 3
SIMPLE MACHINE
SIMPLE MACHINE 2
SIMPLE MACHINE 3
SIMPLE MACHINE 4
Science Form 3 (Chapter 2) Blood Circulation and Transport
Introduction to function of Heart
Credit to http://ptbestari.blogspot.com
The role of the heart is to pump oxygen-rich blood to every living cell in the body. In order to achieve its goal, it must continuously beat for a person’s entire lifespan. Because of its vital role, a non-beating heart always results in death. The human heart beats approximately 80,000 to 100,000 a day and pumps almost 2,000 gallons of blood. This means that in a person’s life lasting 70 to 90 years, the heart beats approximately two to three billion times and pumps 50 to 65 million gallons of blood. Because the heart is so essential for human sustenance, it is made up of a muscle different from skeletal muscle that allows it to constantly beat.
In order for the heart to deliver oxygenated blood to all cells, blood is pumped through arteries. Veins bring deoxygenated blood cells to the lungs, which then are oxygenated, and then sent back to heart. In this way, a continuous cycle is formed of the heart pumping oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood out to their designated destinations, and therefore the heart maintains the circulatory system.

Systole: Stage when the ventricles of heart are contracting resulting in blood being pumped out to the lungs and the rest of the body.
- Thick, muscular walls of both ventricles contract.
- Pressure rises in both ventricles, causing the bicuspid and tricuspid valves to close. Therefore, blood is forced up the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
- The atria relax during this time. The left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary vein, and the right atrium from the vena cava.

Diastole: Stage when the ventricles of the heart are relaxed and not contracting. During this stage, the atria are filled with blood and pump blood into the ventricles.
- Thick, muscular walls of both ventricles relax.
- Pressure in both ventricles falls low enough for bicuspid valves to open.
- The atria contract, and blood is forced into the ventricles, expanding them. The blood pressure in the aorta is decreased, therefore the semi-lunar valves close.





In order for the heart to deliver oxygenated blood to all cells, blood is pumped through arteries. Veins bring deoxygenated blood cells to the lungs, which then are oxygenated, and then sent back to heart. In this way, a continuous cycle is formed of the heart pumping oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood out to their designated destinations, and therefore the heart maintains the circulatory system.

Systole: Stage when the ventricles of heart are contracting resulting in blood being pumped out to the lungs and the rest of the body.
- Thick, muscular walls of both ventricles contract.
- Pressure rises in both ventricles, causing the bicuspid and tricuspid valves to close. Therefore, blood is forced up the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
- The atria relax during this time. The left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary vein, and the right atrium from the vena cava.

Diastole: Stage when the ventricles of the heart are relaxed and not contracting. During this stage, the atria are filled with blood and pump blood into the ventricles.
- Thick, muscular walls of both ventricles relax.
- Pressure in both ventricles falls low enough for bicuspid valves to open.
- The atria contract, and blood is forced into the ventricles, expanding them. The blood pressure in the aorta is decreased, therefore the semi-lunar valves close.





Monday, March 12, 2012
Q&A Form 3 : Chapter 1
d) What are the harmful effect to the respiratory system of the following harmful substances in the
cigarette smoke.
Apakah kesan buruk terhadap sistem pernafasan manusia bagi bahan yang terdapat dalam asap
rokok berikut:
a) Nicotine : cause addiction
b) Tar : blackens the lungs
c) Carbon monoxide : reduce the amount of oxygen in blood
Sains
 Sains Kertas 2
Sains Kertas 2- Johor Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Johor Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Johor Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Johor Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Kedah Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Kedah Trial PMR 2009 (2)
- Kedah Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Kedah Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Kelantan Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Kelantan Trial PMR 2009 (2)
- Kelantan Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Kelantan Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Latih Tubi PMR 2009 (3)
- Melaka Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Melaka Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Melaka Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Motivation (3)
- MRSM Trial PMR 2007 (1)
- MRSM Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- MRSM Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- MRSM Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Negeri Sembilan Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Negeri Sembilan Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Negeri Sembilan Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Negeri Sembilan Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Pahang Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Pahang Trial PMR 2009 (2)
- Pahang Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Pahang Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Perak Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Perak Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Perak Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Perak Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Perlis Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Perlis Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Perlis Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Perlis Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- PMR 2007 (1)
- PMR 2009 (1)
- PMR 2010 (1)
- PPSMI (5)
- Pulau Pinang Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Pulau Pinang Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- QnA Form 3 (4)
- Revision (22)
- Revision Form 3 (20)
- Sabah Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Sabah Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Sabah Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Sarawak Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Sarawak Trial PMR 2009 (2)
- Sarawak Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Sarawak Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- SBP Trial PMR 2007 (1)
- SBP Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- SBP Trial PMR 2009 (2)
- SBP Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- SBP Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Selangor Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Selangor Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Selangor Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Selangor Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Study Tips (2)
- Terengganu Trial PMR 2008 (1)
- Terengganu Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Terengganu Trial PMR 2010 (1)
- Terengganu Trial PMR 2011 (1)
- Trial PMR (1)
- Trial PMR 2007 (1)
- Trial PMR 2008 (13)
- Trial PMR 2009 (19)
- Trial PMR 2010 (13)
- Wilayah Trial PMR 2009 (1)
- Wilayah Trial PMR 2011 (1)
Quick Link Page
06 Oct 2011 MySchoolChildren.com site Quick Link Page Syarat Kelayakan Kemasukan ke Tingkatan 6 Bawah 2012 Permohonan Program Perguruan Ijazah Sarjana Muda Kementerian Pelajaran…Continue reading »
Trial PMR 2011 Bahasa Cina
22 Sep 2011 Kertas Soalan Bahasa Cina Peperiksaan Percubaan PMR 2011. Soalan Percubaan Bahasa Cina Kertas 1, 2 PMR 2011 Negeri Johor …Continue reading »
Trial PMR 2011. Melaka, Pahang, Kelantan dan lain-lain
11 Sep 2011 * * * Perhatian : semua file yang berakhir dengan .rar tidak boleh dibaca terus, anda perlu ekstrak pdf…Continue reading »
Percubaan PMR 2011 Negeri Perak
07 Sep 2011 KERTAS SOALAN PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN PMR 2011 NEGERI PERAK, Ogos 2011. Bahasa Melayu KERTAS 1 Percubaan PMR 2011 Perak. Soalan v2…Continue reading »
Percubaan PMR 2011. Kedah, Terengganu.
30 Aug 2011 Soalan Peperiksaan Percubaan PMR Tahun 2011 Peringkat Negeri Kedah. (Peperiksaan Bersama PMR Negeri Kedah) Bahasa Inggeris KERTAS 1 Trial PMR…Continue reading »
Trial PMR 2011 SBP
24 Aug 2011 KERTAS SOALAN PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN PMR SETARA 2011 SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH DAN SEKOLAH KECEMERLANGAN Bahasa Melayu KERTAS 1 Percubaan PMR 2011…Continue reading »